Trade EU Carbon Credits
The European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) is a cap and trade mechanism that reduces greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. It was introduced in 2005, and covers over 41 percent of EU GHG emissions by 2020. It is designed to promote cost-effective emissions reductions by allowing businesses to decide how to act.
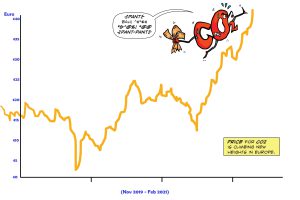
Companies covered by the trade carbon credits are required to hold European Emission Allowances (EUA) for each tonne of CO2 eq emitted during the year. These allowances are allocated to companies free of charge. As more allowances are awarded, the market price for each EUA increases. The price is determined by the supply and demand of these carbon allowances.
To participate in the market, companies must be registered with the EU Registry, a centralized online banking service that is also responsible for issuing and regulating carbon allowances. Once they have completed the registration, they can open Union Registry accounts. They can then buy or sell carbon allowances through auctions.
How to Trade EU Carbon Credits
The process of matching buyers and suppliers is time-consuming and inefficient. It can lead to a lack of liquidity in the carbon market. Hence, it is important for companies to engage actively with regulatory changes that are expected to be implemented in the future. They may also need to supplement abatement efforts. This would ensure a low-cost and efficient compliance with the GHG policy.
Since its introduction, the European Emissions Trading System has undergone several significant changes. It now includes not only power generation plants, but also civil aviation, airlines and railways. In addition, it also offers extra allowances for industries exposed to carbon leakage, such as steel and cement installations.
In order to reduce emissions, companies are encouraged to adopt new energy sources and technologies, including renewable energies. They can also postpone their action or buy emissions permits from other companies. The EU ETS has helped companies to achieve a significant reduction in their greenhouse gas emissions.
While the EU ETS remains the largest carbon market in the world, it has seen a number of changes in the past few years. These include the temporary removal of 900 million permits from the auction in 2014-2016 and the backloading initiative to reduce the surplus of 2 billion allowances.
Nevertheless, the market remains characterized by scarce financing and inadequate risk-management services. This makes the process of locating trustworthy sources of high-quality carbon credits more difficult. To overcome this obstacle, it is recommended that a robust voluntary market be developed. It is advisable to set up a third-party organization to define a common attribute taxonomy, and develop a market based on the attributes. This would increase the supply of carbon credits and make it easier for organizations to locate reliable sources.
Although the carbon market is a highly regulated system, it can be a powerful tool for driving standards internationally. By making it more competitive, organizations will have an incentive to reduce their emissions. For example, companies can purchase credits from emission-reducing projects under the Kyoto Protocol’s Clean Development Mechanism.
